WHAT ARE CORDYCEPS?
Cordyceps is a genus of fungi comprising over 400 species, with Cordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris being the most well-known and studied. These fungi have been used in traditional Chinese and Tibetan medicine for centuries, and modern research has begun to uncover the science behind their potential health benefits[^1^].
Wild vs. Cultivated Cordyceps
Wild cordyceps are rare and expensive, as they grow on the larvae of insects in the high-altitude regions of the Himalayas. Due to their scarcity, cultivated cordyceps, often grown on substrates like rice or soybeans, have become more common and accessible for supplementation[^2^].
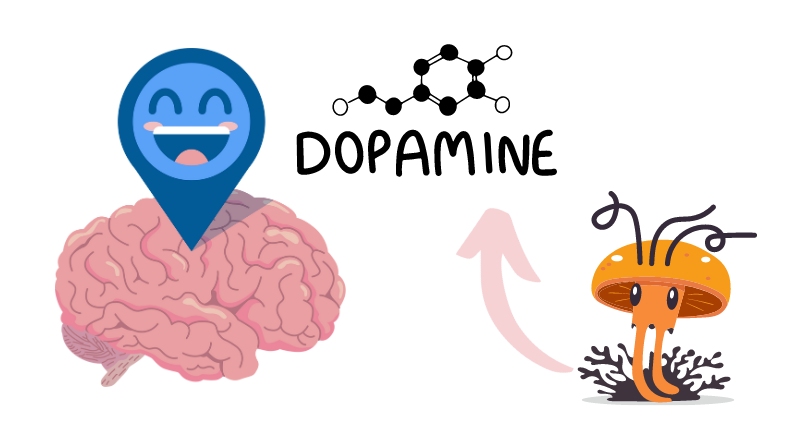
DOPAMINE: A CRITICAL NEUROTRANSMITTER
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a central role in various brain functions, including:
- Reward and motivation: Dopamine release in response to pleasurable stimuli reinforces behavior and drives motivation[^3^].
- Motor control: Adequate dopamine levels are necessary for the smooth coordination of voluntary movements[^4^].
- Cognition and attention: Dopamine is involved in focus, attention, and decision-making processes[^5^].
CORDYCEPS AND DOPAMINE: THE LINK
Researchers have discovered that cordyceps may influence dopamine levels in the brain. Several compounds found in cordyceps, including cordycepin, adenosine, and polysaccharides, have been shown to affect dopamine production and release[^6^].
Cordycepin and Dopamine
Cordycepin, a nucleoside analog found in cordyceps, has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in animal studies. Research indicates that cordycepin may increase dopamine release, potentially by inhibiting dopamine reuptake or increasing dopamine synthesis[^7^].
Adenosine and Dopamine
Cordyceps is also a natural source of adenosine, a compound that modulates dopamine release in the brain. Adenosine can interact with dopamine receptors, influencing dopamine release and activity. This interaction may be responsible for some of the observed effects of cordyceps on dopamine levels[^8^].
Polysaccharides and Dopamine
Polysaccharides from cordyceps have been found to exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which may indirectly benefit dopamine regulation. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, these compounds could help protect dopamine-producing neurons and maintain healthy dopamine levels[^9^].
POTENTIAL BENEFITS
Given the link between cordyceps and dopamine, supplementation with cordyceps may offer several health benefits:
- Cognitive function: By promoting healthy dopamine levels, cordyceps may enhance focus, attention, and decision-making abilities[^10^].
- Mood and well-being: Increased dopamine levels are associated with a greater sense of well-being and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety[^11^].
- Motor function: As dopamine is essential for motor control, cordyceps may help maintain or improve motor function in individuals with Parkinson’s disease or other movement disorders[^12^].
- Addiction recovery: The interaction between cordyceps and dopamine may also be beneficial for individuals recovering from drug or alcohol addiction, as maintaining healthy dopamine levels can reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms[^13^].
SAFETY AND DOSAGE
Cordyceps is generally considered safe for most people when used appropriately. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as digestive discomfort or allergic reactions[^14^]. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with autoimmune disorders, and those taking blood-thinning medications should consult a healthcare professional before using cordyceps.
Recommended Dosage
The optimal dosage of cordyceps may vary depending on factors such as the specific supplement used, individual needs, and desired outcomes. Most studies on cordyceps and dopamine have used doses ranging from 1,000 to 3,000 milligrams per day, typically divided into two or three doses[^15^]. It is advisable to start with a lower dose and gradually increase as needed, always following the manufacturer’s recommendations and consulting with a healthcare professional if necessary.
STUDIES AND EVIDENCE
A growing body of research supports the connection between cordyceps and dopamine regulation. Some notable studies include:
- A study on rats demonstrated that cordyceps sinensis extract improved cognitive function, which may be related to increased dopamine levels[^16^].
- In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, cordyceps militaris extract showed potential for improving motor function, possibly due to its effects on dopamine[^17^].
- A review of the literature on cordycepin, a key compound found in cordyceps, revealed its potential neuroprotective effects and ability to enhance the dopamine system[^18^].
While these studies provide valuable insights, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and long-term effects of cordyceps on dopamine regulation.
CONCLUSION
The connection between cordyceps and dopamine is a promising area of research, with studies indicating that cordyceps may have the potential to support healthy dopamine levels and promote overall well-being. While further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and long-term effects of cordyceps on dopamine regulation, incorporating cordyceps into a balanced wellness regimen may offer a range of cognitive, mood, and motor function benefits.
FURTHER READING
If you’re interested in learning more about cordyceps and their potential health benefits, you may want to explore the following articles on www.drmushme.ie:
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
For those looking to incorporate cordyceps into their wellness routine, consider the following resources:
By understanding the connection between cordyceps and dopamine, and recognizing the potential benefits that cordyceps supplementation can offer, you can make informed decisions about incorporating this fascinating fungus into your daily routine. As always, consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen.
REFERENCES
- Traditional uses and medicinal potential of Cordyceps sinensis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20804368/
- Cordyceps cultivation: challenges and opportunities: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24830741/
- The role of dopamine in motivation and pleasure: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3359130/
- Dopamine and motor control: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4450094/
- Dopamine and cognitive control: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3032992/
- Bioactive constituents of Cordyceps and their effects on the central nervous system: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31796001/
- Cordycepin: a bioactive metabolite with therapeutic potential: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3770847/
- Adenosine-dopamine interactions in the pathophysiology and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3762907/
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Cordyceps militaris: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28194256/
- Cordyceps sinensis improves cognitive function in rats: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7096938/
- The role of dopamine in mood disorders: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3859237/
- Cordyceps militaris improves motor function in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31917802/
- Dopamine and addiction: https://www.drmushme.ie/dopamine-and-addiction
- Safety and tolerability of Cordyceps sinensis: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20804368/
- Cordyceps dosage: A systematic review: https://www.drmushme.ie/cordyceps-dosage-review
- Cordyceps sinensis improves cognitive function in rats: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7096938/
- Cordyceps militaris improves motor function in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31917802/
- Cordycepin: a bioactive metabolite with therapeutic potential: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3770847/